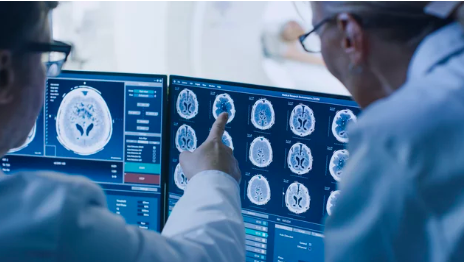
કેન્સર શું છે ? કેન્સરને સમજવા અને કેન્સર સામે લડાઈ
આજે, અમે વિશ્વભરના અસંખ્ય જીવનને સ્પર્શતા વિષય વિશેની અમારી સમજને વિસ્તૃત કરવા માટે પ્રવાસ શરૂ કરી રહ્યા છીએ: કેન્સર.
કેન્સર
તે એક એવો શબ્દ છે જે ભય અને અનિશ્ચિતતાને ઉત્તેજિત કરે છે, પરંતુ કેન્સર બરાબર શું છે? તે કેવી રીતે વિકસિત થાય છે, અને તેને રોકવા અને સારવાર માટે આપણે શું કરી શકીએ? ચાલો આ પ્રશ્નો અને વધુમાં ડાઇવ કરીએ.
કેન્સરનો પરિચય
કેન્સર શરીરની અંદર કોષોની અસામાન્ય વૃદ્ધિ અને પ્રસાર દ્વારા વર્ગીકૃત થયેલ રોગોના જૂથનો ઉલ્લેખ કરે છે. આ બદમાશ કોષો તંદુરસ્ત પેશીઓમાં ઘૂસણખોરી કરી શકે છે અને તેનો નાશ કરી શકે છે, જો અનચેક કરવામાં આવે તો સંભવિતપણે ગંભીર જોખમો ઉભી કરી શકે છે. પરંતુ શું આ કોષોને આટલા જોખમી બનાવે છે? ચાલો કેન્સરના લક્ષણો વિશે જાણીએ.
કેન્સરના લક્ષણો શું છે ?
અનિયંત્રિત કોષ વૃદ્ધિ: કેન્સરના કોષો સામાન્ય નિયંત્રણો વિના વિભાજીત અને ગુણાકાર કરે છે જે કોષની વૃદ્ધિને નિયંત્રિત કરે છે.
આક્રમણ: આ કોષોમાં આસપાસના તંદુરસ્ત પેશીઓ પર આક્રમણ કરવાની અને નાશ કરવાની ક્ષમતા હોય છે.
મેટાસ્ટેસિસ: કદાચ સૌથી ચિંતાજનક, કેન્સરના કોષો શરીરના અન્ય ભાગોમાં ફેલાઈ શકે છે, જે તેમના મૂળ સ્થાનથી દૂર રોગની નવી જગ્યાઓ સ્થાપિત કરે છે.
કેન્સરના કારણો અને કેન્સર કેમ વિકસે છે ?
કેન્સર કોશિકાઓના ડીએનએમાં ફેરફારો અથવા પરિવર્તનોથી ઉદ્ભવે છે.
આ ફેરફારો વિવિધ પરિબળો દ્વારા સંચાલિત થઈ શકે છે: આનુવંશિક પરિબળો: વારસાગત પરિવર્તન વ્યક્તિઓને કેન્સરનું જોખમ લાવી શકે છે.
પર્યાવરણીય એક્સપોઝર: તમાકુનો ધુમાડો, યુવી રેડિયેશન અને અમુક રસાયણો જેવા કાર્સિનોજેન્સ ડીએનએને નુકસાન પહોંચાડી
શકે છે. જીવનશૈલીની પસંદગીઓ: ખરાબ આહારની આદતો, બેઠાડુ જીવનશૈલી અને વધુ પડતા આલ્કોહોલનું સેવન કેન્સરના જોખમમાં ફાળો આપે છે.
ચેપ: અમુક વાયરલ ચેપ, જેમ કે એચપીવી અને હેપેટાઇટિસ બી, કેન્સરના વિકાસને પ્રોત્સાહન આપી શકે છે.
યજમાન: “આનુવંશિક પરિવર્તનનો સંચય ઘણીવાર કેન્સરની શરૂઆતને આધાર આપે છે.”


કેન્સરના પ્રકાર શું છે?
કેન્સરના ઘણાં વિવિધ પ્રકારો છે, જે કોષોમાંથી ઉત્પન્ન થાય છે તેના આધારે વર્ગીકૃત કરવામાં આવે છે:
કાર્સિનોમાસ: આ ત્વચા અથવા અવયવોના અસ્તરમાંથી ઉદ્ભવે છે.
લ્યુકેમિયા: આ કેન્સર રક્ત અને અસ્થિ મજ્જાને અસર કરે છે.
લિમ્ફોમસ: આ રોગપ્રતિકારક તંત્રમાં શરૂ થાય છે. સાર્કોમાસ: આ હાડકાં અને સ્નાયુઓ જેવા જોડાયેલી પેશીઓમાંથી બહાર આવે છે.
કેન્સરની અસર શું છે ?
કેન્સર વ્યક્તિઓ અને સમાજ પર વ્યાપક અસર કરે છે. શારીરિક, ભાવનાત્મક અને નાણાકીય બોજો જબરજસ્ત હોઈ શકે છે, જે દર્દીઓ, પરિવારો અને સંભાળ રાખનારાઓને સમાન રીતે અસર કરે છે.
આપણે કેન્સરની તપાસ અને નિવારણ કેવી રીતે કરીએ
નિયમિત સ્ક્રિનિંગ અને સમયસર તપાસ કેન્સરની પ્રગતિને અટકાવવામાં મુખ્ય છે.
તંદુરસ્ત જીવનશૈલી અપનાવવી, જાણીતા જોખમી પરિબળોથી દૂર રહેવું અને કેન્સર-સંબંધિત ચેપ સામે રસીકરણ મેળવવાથી કેન્સરની સંવેદનશીલતા નોંધપાત્ર રીતે ઓછી થાય છે.

કેન્સરની સારવારની પદ્ધતિઓ શું છે
કેન્સરની સારવારમાં પ્રગતિ અસરગ્રસ્તો માટે આશા અને વિકલ્પો પ્રદાન કરે છે:
સર્જરી: કેન્સરગ્રસ્ત ગાંઠોને શસ્ત્રક્રિયા દ્વારા દૂર કરવી.
કીમોથેરાપી: કેન્સરના કોષોને મારવા માટે ફાર્માસ્યુટિકલ એજન્ટોનો ઉપયોગ કરવો.
રેડિયેશન થેરપી: ઉચ્ચ-ઊર્જા રેડિયેશન સાથે કેન્સરના કોષોને લક્ષ્ય બનાવવું. ઇમ્યુનોથેરાપી: કેન્સર સામે લડવા માટે શરીરની રોગપ્રતિકારક શક્તિનો લાભ લેવો.
“દરેક દર્દીના કેન્સરના પ્રકાર અને તબક્કાને અનુરૂપ સારવાર યોજનાઓ હિતાવહ છે.”
નિષ્કર્ષ
કેન્સર એક બહુપક્ષીય પડકારનું પ્રતિનિધિત્વ કરે છે જેમાં નિવારણ, નિદાન અને સારવારનો સમાવેશ કરતા સર્વગ્રાહી અભિગમની જરૂર હોય છે.
તે એક જટિલ અને વિનાશક રોગ છે જે કોઈપણ વ્યક્તિને અસર કરી શકે છે, વય અથવા પૃષ્ઠભૂમિને ધ્યાનમાં લીધા વિના.
અસરકારક સારવાર અને નિવારક પગલાં વિકસાવવા માટે કેન્સરની વૃદ્ધિ, આક્રમણ અને મેટાસ્ટેસિસની મૂળભૂત પદ્ધતિઓને સમજવી મહત્વપૂર્ણ છે.
જાગરૂકતા વધારીને અને સંશોધનના પ્રયાસોને સમર્થન આપીને, અમે એવા ભવિષ્ય તરફ કામ કરી શકીએ છીએ જ્યાં કેન્સર હવે જીવલેણ નિદાન નથી, પરંતુ વ્યવસ્થાપિત સ્થિતિ છે. કેન્સરના અસંખ્ય પાસાઓને સમજીને, આપણે આપણી જાતને આપણા સ્વાસ્થ્ય અને સુખાકારીને લગતા માહિતગાર નિર્ણયો લેવા માટે સક્ષમ બનાવીએ છીએ.
ચાલો કેન્સર સામેના આપણા ધર્મયુદ્ધમાં જાગ્રત, માહિતગાર અને એકીકૃત રહીએ. “સ્વાસ્થ્યને સમજવું” પર અમારી સાથે જોડાવા બદલ આભાર.
અમારા આગામી એપિસોડ માટે જોડાયેલા રહો, જ્યાં અમે અમારા સ્વાસ્થ્ય અને સુખાકારીની જટિલતાઓનું અન્વેષણ કરવાનું ચાલુ રાખીશું. ત્યાં સુધી, સ્વસ્થ રહો અને માહિતગાર રહો.
કેન્સર શું છે ? કેન્સરને સમજવા અને કેન્સર સામે લડાઈ Read More »
Understanding Cancer